What is Gum Disease
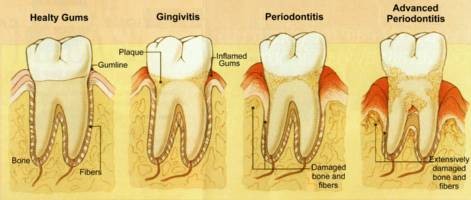
With more than two-thirds of all adults showing some form of gum infection, gum disease is one of the most common infections affecting people today. Gum disease commonly refers to a wide spectrum of infections that affect the soft and hard tissue of the mouth. We can generally separate the disease into gingivitis or periodontitis. Gingivitis is seen as the early stages of gum infection where no long-term damage to the gums or deeper supporting structures has taken place. Gingivitis is considered reversible. However if gingivitis is allowed to continue, periodontal disease can develop. In periodontal disease there is destruction of the supporting tissues, including the gums, bone and periodontal ligaments (the fibres that hold the teeth in the jaw). Eventually the destruction could cause the teeth to become loose and even be lost.
More importantly, research has associated periodontal infection to several serious medical problems; including heart disease, diabetes and stroke. This underlines the need for a comprehensive approach to the treatment of gum disease, as the impact it has on general health can be significant. As ongoing research continues to define how periodontal disease is associated with these and other health problems, oral health maintenance is essential.
What Can Cause Infection to Advance
People with periodontal disease have low resistance to periodontal bacteria. This causes an ongoing gum infection that grows in "bursts" of activity. Each time it grows, more support for your teeth is lost. Some risk factors that can cause this to occur may include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Dental plaque
- Genetic factors
- Stress or tension
- Diet
- Age
- Illness
- Bad bite
- Systemic Illness
- Smoking / Tobacco
- Grinding
- Open mouth breathing
- Medications
- Xerostomia
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Perimenopause or Menopause
Symptoms of Periodontal Infection
Periodontal infection is usually painless until it reaches an advanced stage. However, there are some symptoms which can indicate the presence of periodontal infection. These may include:
- Red or swollen gums
- Bleeding when brushing (pink toothbrush), or at other times
- Aching, itchy, sore or tender gums
- Receding gums (teeth beginning to look longer)
- Pus between your teeth and gums when you press down on the gums
- Bad breath
- Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
- Any change in the fit of partial dentures
- Loose, separating or protruding teeth
- Spaces between teeth
If you notice any of the above warning signs of periodontal infection, please contact your dentist and ask for a periodontal evaluation.
Important Note: Your gums can look and feel quite normal and yet deep pockets of periodontal infection can still be present. To be certain about any periodontal disease, ask your dentist or periodontist to examine your gums for signs of infection.